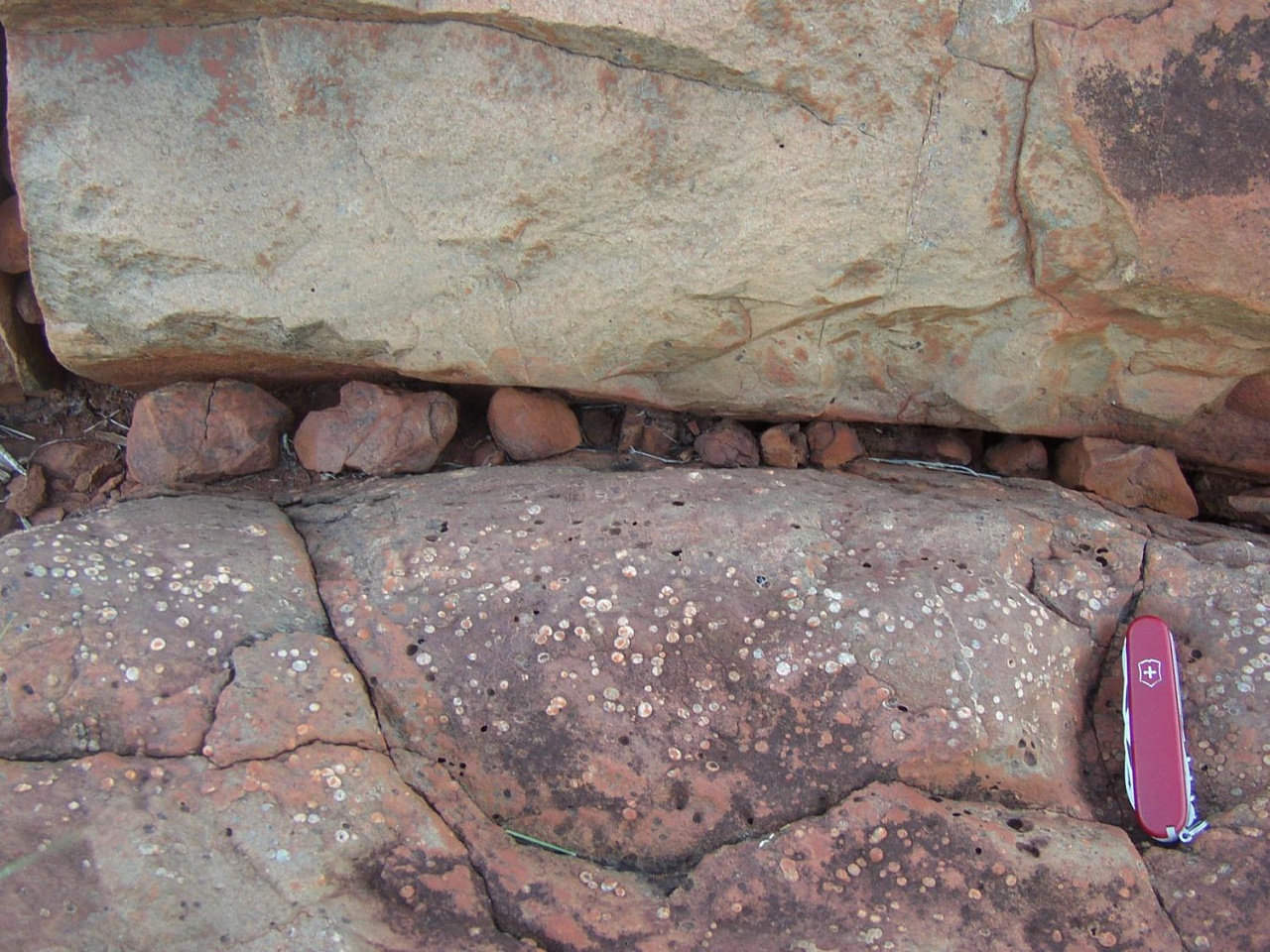
The air pressure on Earth 2.7 billion years ago was no more than half of what it is today.
This, according to new research which has analyzed air bubbles that once formed in lava in what is now Australia. The researchers can make his conclusion as there is a direct correlation between the size of the bubble and the air pressure. Simply put the larger the bubble, the lower the air pressure.
Previous research suggests that the Sun was much cooler at this time than it is now. Therefore, it has been a bit of a paradox how the Earth could be kept warm enough and be favorable for life.
“For the longest time, people have been thinking the atmospheric pressure might have been higher back then because the sun was fainter,” said lead author Sanjoy Som, who did the work as part of his UW doctorate in Earth and space sciences. “Our result is the opposite of what we were expecting.”
These new findings appear to confirm the hypothesis that there must have been considerable amounts of greenhouse gasses on the planet at this time, such as methane. The methane as a very potent greenhouse gas would be effective at keeping the heat trapped in the atmosphere of the Earth.
This ramped up greenhouse effect would enable life to survive and indeed prosper despite the thin atmosphere. The research is another step to better understand the evolution of life before Earth got an atmosphere with oxygen.
The researchers will next look for other suitable rocks to confirm the findings and learn how atmospheric pressure might have varied through time.
________________
Earth’s air pressure 2.7 billion years ago constrained to less than half of modern levels. Nature Geoscience
________________________________