Who Were the Rain Deer People, this is the question asked by scientists after several new findings in China of a previously unknown people.
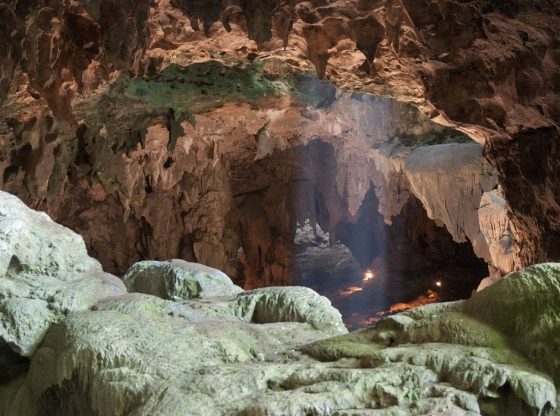
The Australian and Chinese scientists have found the remains of these previously unknown prehistoric people who seemingly lived in caves at several locations throughout southern China around 14,500 to 11,500 years ago. Radiocarbon dated using charcoal found at the fossil deposits.
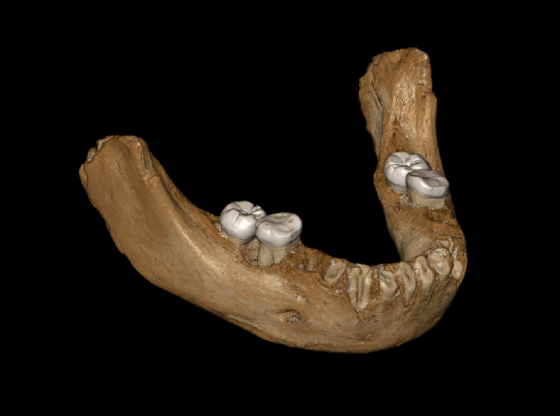
The first remains were found in 1979 with a partial skull in Longlin Cave in the Guangxi Zhuang region of China. Then further human remains have been excavated from Maludong (the Red Deer Cave) in Yunnan Province.
Homo Sapiens or something else?
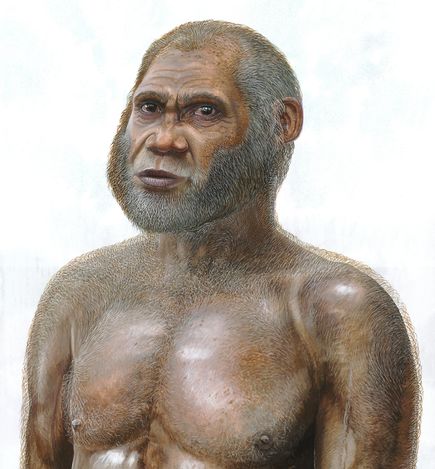
At first, the remains were thought to be Homo Sapiens in origin, but then the bones and skulls from the smallest of five individuals were found to be unlike anything is seen before. They have a special blend of modern and primitive features and some very unique features.
They have very big eyebrow arches, wide cheekbones, and a thick skull. These are all typical features for those human types that lived several hundred thousand years ago. Their brain is smaller compared to Homo Sapiens. But their frontal lobe, which is thought to include personality and behavior, is indeed as big as ours. Their brain’s rearmost part, which handles sensory input, is much more primitive, though.
The scientists do not dare to classify them as a new Homo species as of yet. They, therefore, call them the Red Deer People, named after the many red deer remains found in the caves.
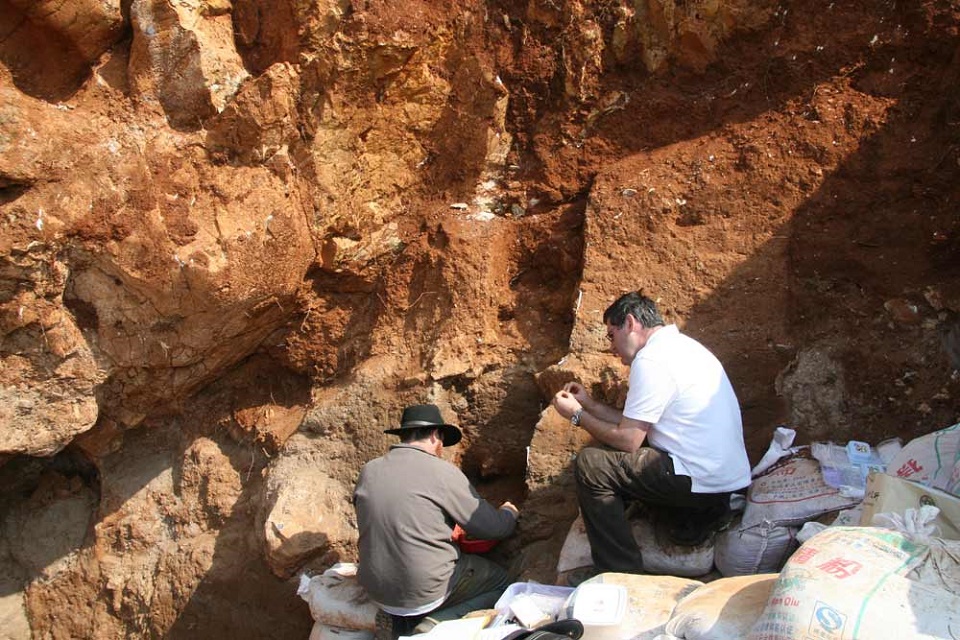

The study’s (published in PLoS One) lead researcher Darren Curnoe is leaning towards that they actually belong to a whole new line on our family tree. But other researchers argue that they belong to an unusual variant of our own species. Perhaps they are the descendants of humans that have heavily interbreed with other more primitive Humans, such as Homo Erectus.
But the scientists now hope to settle the issue with DNA analysis.
Shared Earth
Research has in recent years revealed that we have indeed shared the Earth with many of our distant cousins. That we were not the only humanoids walking the earth very recently.
With several new species that have been discovered, including the Denisovans, Homo Floresiensis (“The Hobbit”). Both probably walking the earth simultaneously with our own species and Homo Neanderthals.
Our own DNA also let out of the above, since evidence of interbreeding with Neanderthals and other human species are still present in modern humans.
_______________
Human Remains from the Pleistocene-Holocene Transition of Southwest China Suggest a Complex Evolutionary History for East Asians
______________________________