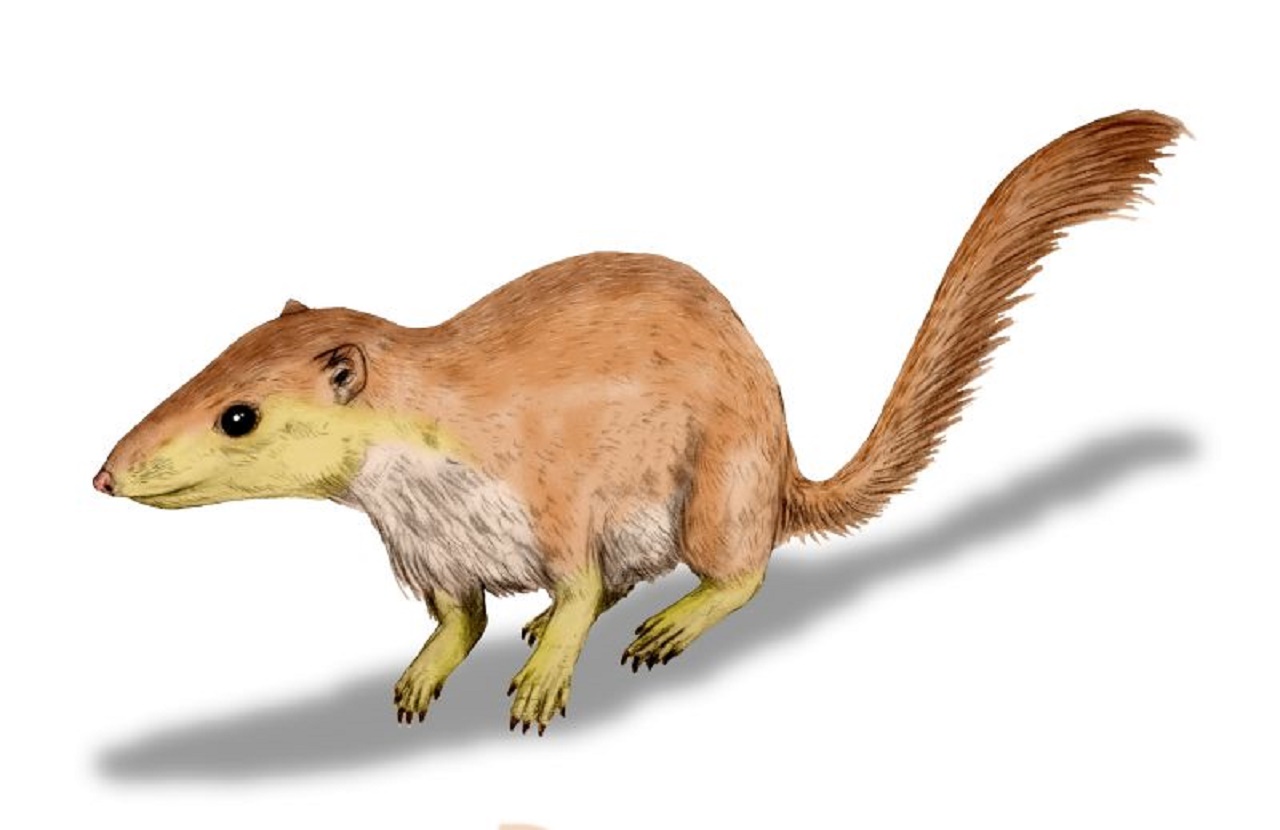
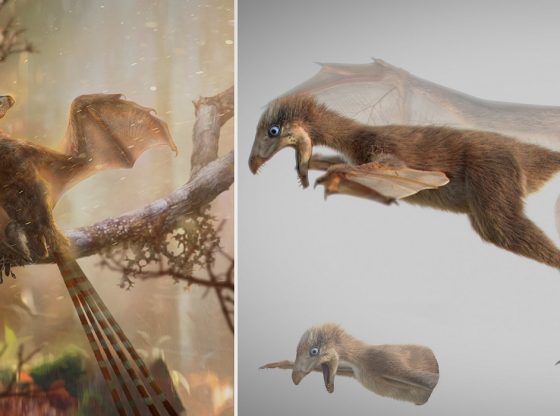
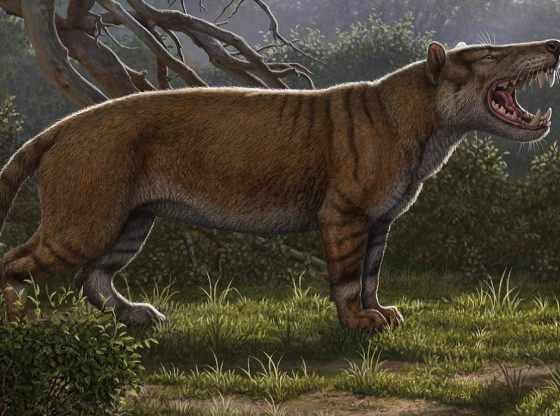
Our perception of mammals during the time that dinosaurs dominated the planet has been that of obscure and small animals with little impact on the ecosystem.
Maybe we need to change this notion since new research shows that mammalian development began before the great extinction event 66 million years ago when the Earth was struck by an asteroid.
The American researchers show that mammalian evolutionary development took off some 10 to 20 million years before the dinosaurs became extinct. The researchers suggest that these early mammals, our predecessors, were not meaningless little animals. They instead indicate great diversity.
Unexpected Diversity
The previously accepted notion was that mammal genetic evolution and diversity took off just after the asteroid impact and this may still be true. But this notion was based on the only mammalians fossil findings of small insectivorous animals that were all quite similar. In recent years, however, more and more mammals have been found, some as big as dogs.
The researchers analyzed the molars on hundreds of very early mammalian fossils in museum collections.They discovered that the mammals that existed during the age of dinosaurs indicate very varied tooth shapes which imply that they ate a varied diet. This varied diet turned out to be a key leading to another unexpected discovery.
The mammals not only earlier than previously, though, they were also affected by the selective extinction that the asteroid implied at the same time the dinosaurs died out. Omnivores that ate a varied diet seemed to be better equipped to survive than picky eaters, with more narrow and specialized sources of food .
Mammalian Evolution Linked to Plant Evolution?
Why mammals indicate such a great diversity and evolution during the age of dinosaurs is not known. But one theory is that there is a possible link between mammalian development and plants that evolved during the same period.
It could be that flowering plants evolved new seeds and fruits available for mammals to eat – a synergistic effect – that spurred the development of both. If these plants developed concurrently with new insects that pollinated them, insects may have been food for early mammals David Grossnickle, one of the authors of the study, wrote in a press release.
The mammals were already on the rise before the asteroid impact and the dinosaur extinction presented a set table for mammals to become the dominant animals on the planet.
__________________________