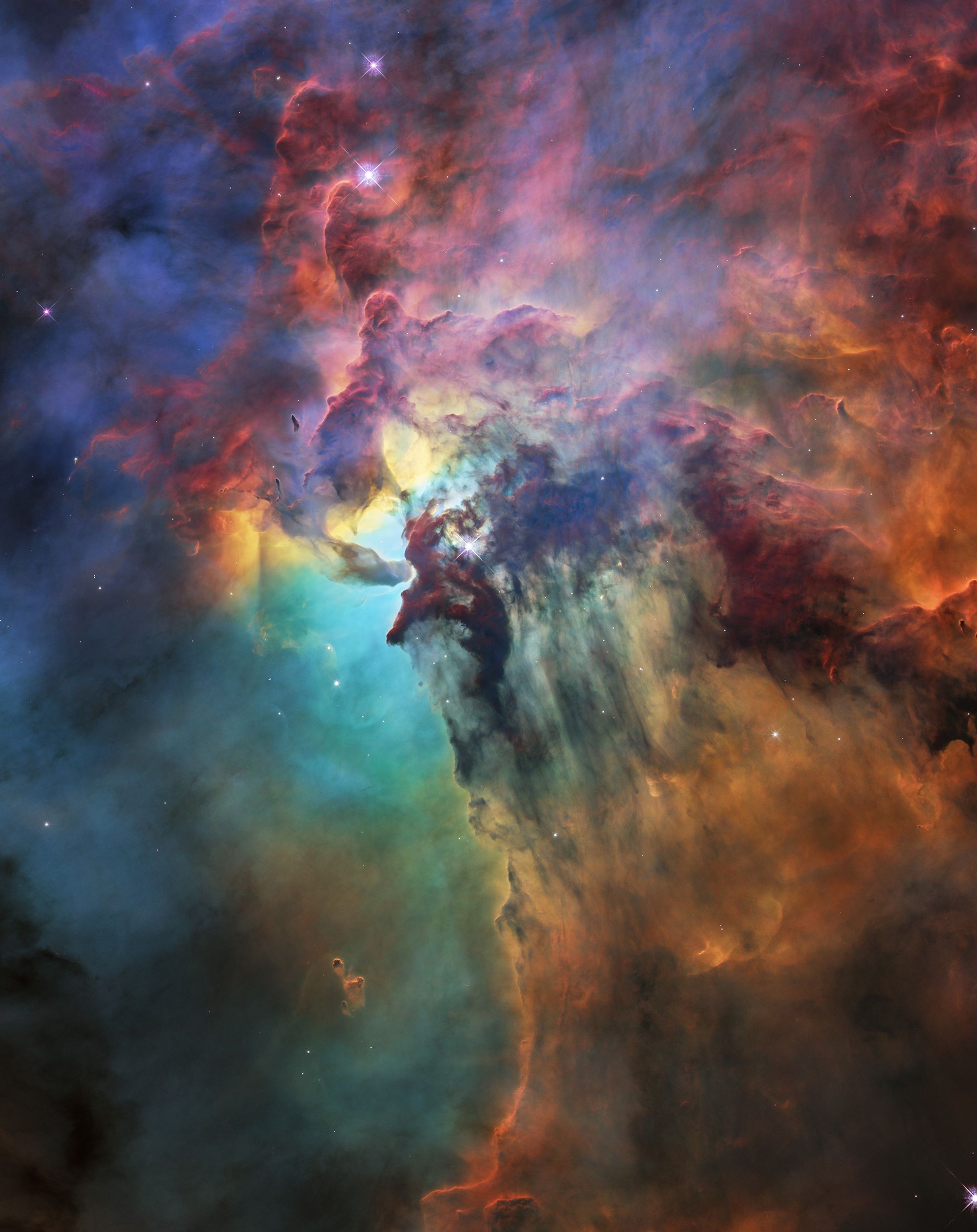
Hubble is 28 years old and, to celebrate its big day, it shows us a nebula, the universe’s nursery, as we have never seen it before.
Nebulae are huge areas of matter and gas where stars are born. A nearby nebula is the so-called Lagoon Nebula, and it is currently forming stars from densely packed gases and space ponds.
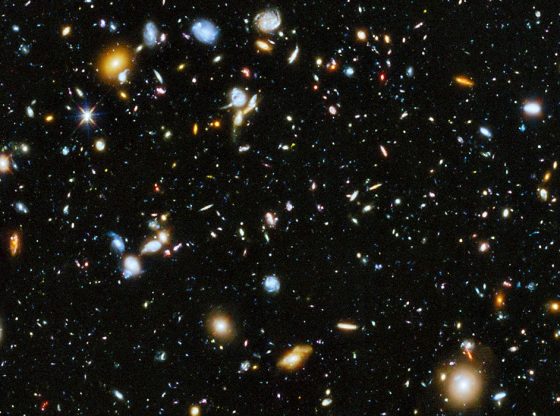
The Hubble telescope has long photographed both nebulae as well as galaxies several billion years away. With the help of the new pictures taken by the Hubble telescope, we can now see places where star formation is happening more clearly than ever.
NASA’s space telescope captures both ordinary light – light seen by us humans – and infrared light. Since Infrared light is absorbed to a lesser degree by the interstellar stuff on its way between the nebula and the Hubble telescope, which makes it possible to see through the fog.
But since the infrared light can not completely absorb the substance, the astronomers can also see where the stars are in the nebulous depending on the size and temperature of the stars.
The stars that appear to be redder have more matter in between them and the telescope and are therefore located deeper in the nebulae. The reverse is true for those stars that aren’t located as deep in the nebulae, and therefore appear to be more white. The astronomers used this data to create an animation that shows a colorful journey through the Lagoon Nebulae.
Hubble was launched in space in 1990 and five years later, its first photos surprised a whole field of research. The telescope has since continued to deliver. The image called Hubble Deep Field showed 3,000 galaxies and for the first time astronomers got to see how these stars came into being in the beginning of the universe.
Hubble has helped astronomers to explore more distant parts of space, galaxies as well as Nebulae. The fact that it has been active in space for almost 30 years is remarkable,
The telescope is planned to be active until 2025, but it will eventually break apart due to all the space junk constantly hitting it. Space can be a rather hostile place.