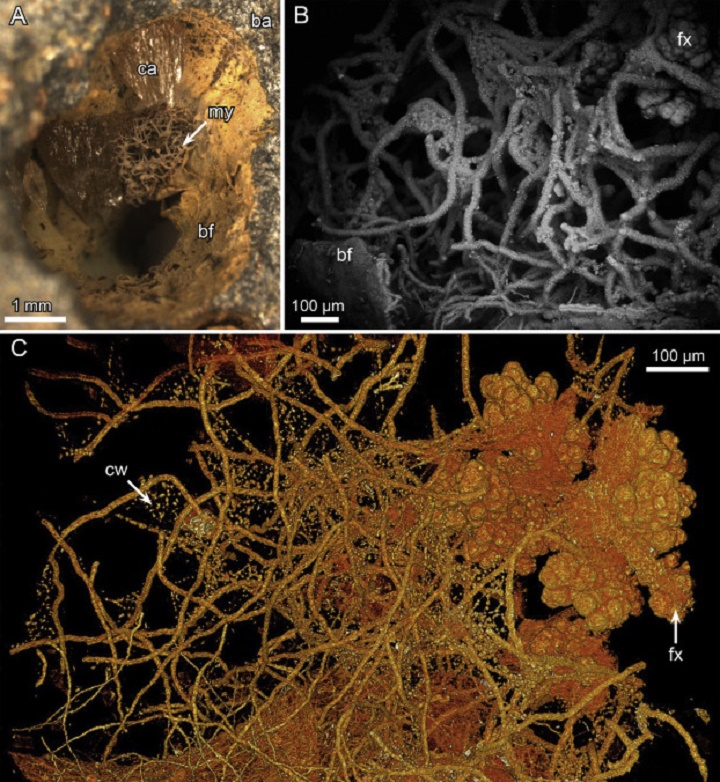
Fungi thrives deep down in the Earth’s crust under the oceans, this according to new research.
It has been established in recent years that fungus can live in both sea and freshwater. But it still surprised researchers who discover that samples from the bedrock thousand of meters under the seabed contained large quantities of fungi.
These are environments that man until just 30 years ago thought was totally devoid of life. Some bacteria and archaea live near hot springs, but that more complex organisms like fungi can thrive deep beneath the seabed is totally new to science.
Great Diversity
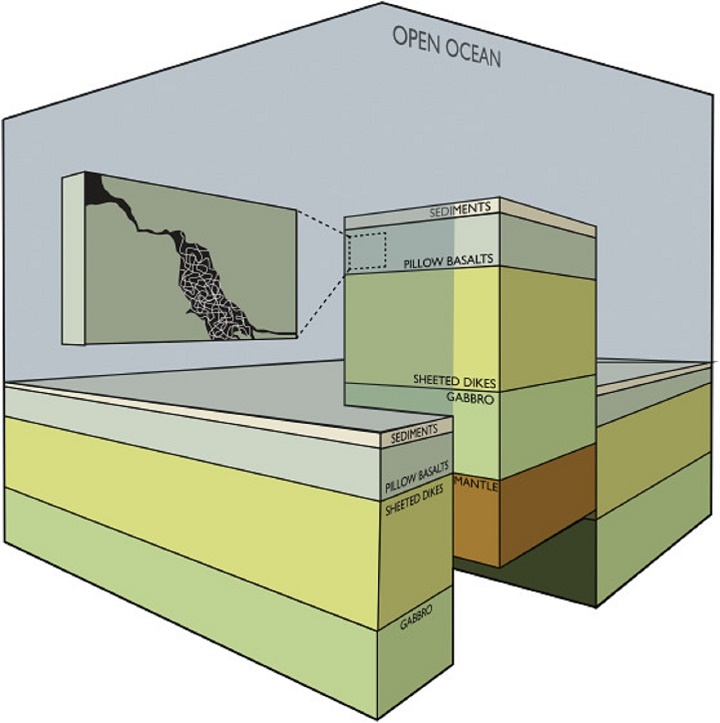
After examining the samples from all the world’s oceans, the researchers conclude that the Earth’s crust is, in fact, the world’s largest environment for fungus to live. And diversity is great. All the major fungal groups are represented.
This means that several relatives to more well-known edible mushrooms are indeed living deep in the depths in total darkness, and probably without oxygen.
The fungi can handle these tough conditions by living in symbiosis with bacteria and archaea, these oxidize iron, reduce sulfates, and thereby supply the fungus with food. The scientists speculate that the fungi produce carbon dioxide that the bacteria and archaea need to survive.
Fossils and Live Specimen
The fungi that the scientists have found are very small and very old fossils. The oldest is assessed to be around 458 million years.
But the scientists are hopeful that they will soon be able to collect live sponge. The reason to why they have not yet succeeded is that it has not been possible to obtain the samples without going into seawater, which made it impossible to get the material without being contaminated.
There might be fungi even deeper than 1,000 meters below the seabed, but so far it is technically impossible to drill deeper.
_____________
The igneous oceanic crust – Earth’s largest fungal habitat?
__________________________