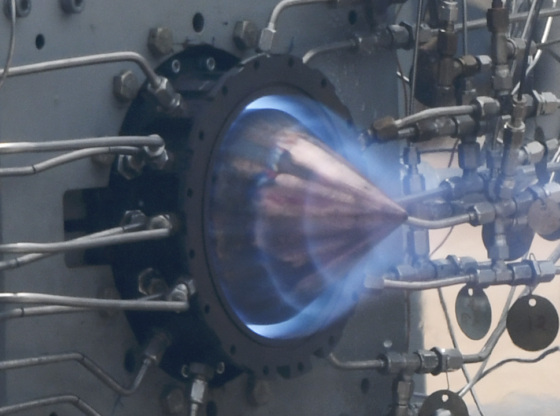
The Japanese space agency JAXA is planning to build a space base on the moon in 2030, and they plan on doing so with the help of heavy robotic machines from Kajima.
Several space agencies have once again set their eyes on the moon. A new space race is underway and NASA (US), ESA (Europe), Roscosmos (Russia) and CNSA (China) all plan to build bases on the moon and later Mars. Now the Japanese space agency JAXA is joining the others.
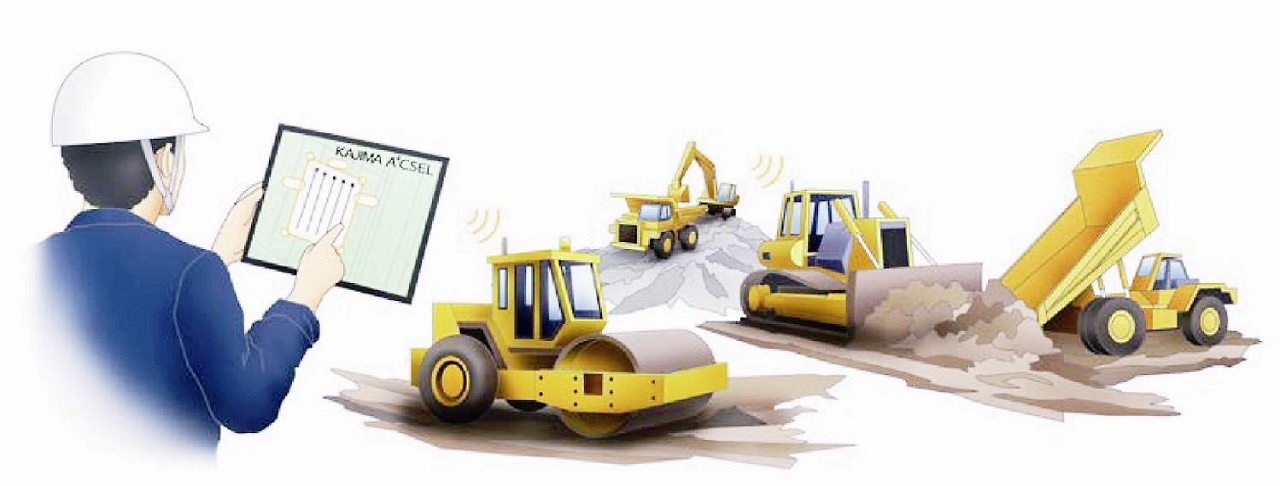
Along with the construction machine manufacturer Kajima – they are to develop technology that Kajima has already started to introduce in their machines, called A4CSEL (Automated Autonomous Advanced Accelerated Construction System for Safety, Efficiency, and Liability).
The technology has been tested when doing construction work of dams in Fukuoka and Oita, in Japan. JAXA now wants to further develop the technology for use in space activities.
The technology makes it possible to control the heavy machines remotely via a touch-pad. However, as the distance to the moon makes for some delay of the signals, Kajima will further develop its technology so that the machines can perform their tasks autonomously.
Since construction machines are heavy in their current design, they are not really suitable for transport to other celestial bodies. At least not in one piece. But since gravity is much lower on the moon, the need for the machines to be heavy are also reduced. Aiming to reduce the size but keep the capacity intact – JAXA, Kajima and the machine manufacturer Taguchi has launched a project together to produce very lightweight construction machines.
_______________
JAXA, select 31 projects for FY2015 Request for Proposal
______________________________