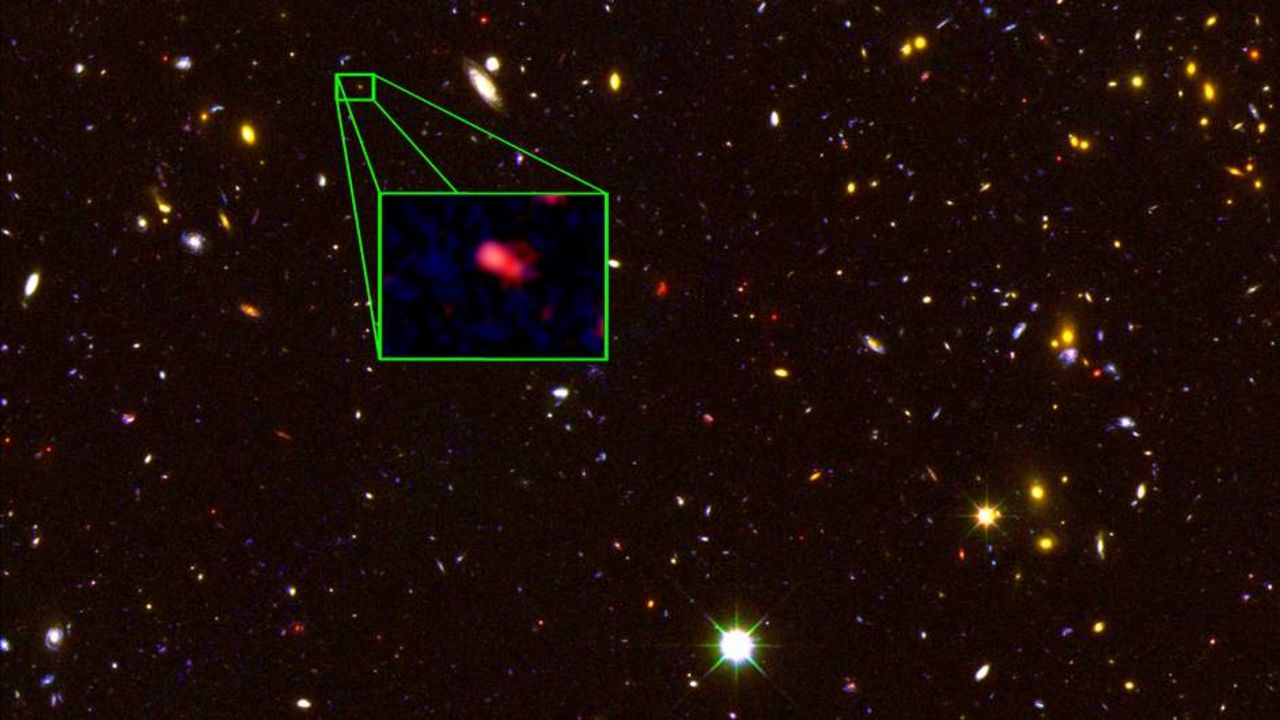
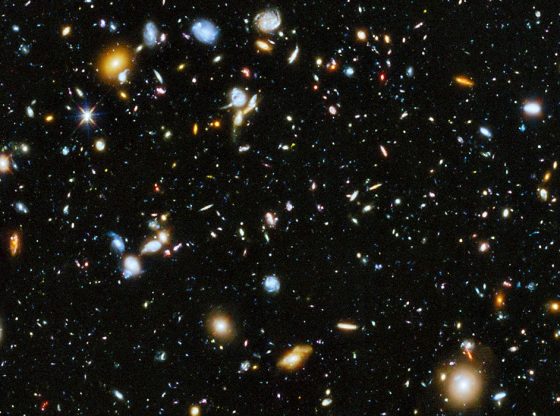
Astronomers have discovered the most distant galaxy detected so far. As immensely distant this galaxy it is in space, so it is in time.
The galaxy is called z8-GND-5296 and the light from the galaxy have been traveling for about 13 billion years. As it is 13 billion light-years away from us.
It is believed that Z8-GND-5296 was formed only about 700 million years after the universe was created in the so-called Big Bang.
The astronomers used data collected by the Hubble Space Telescope and observations from the Keck I telescope at the Keck Observatory in Hawaii.
The galaxy is at a redshift of 7.51, and its neighbor is the second most distant galaxy with a redshift of 7.2. Redshift happens when the light (or electromagnetic radiation) of an object increased in wavelength due to the fact that it is moving away from the observer.
The change in wavelength is related to the so-called Doppler effect, named after Christian Doppler. Just as you hear a car moving past and the sound of it changing its position relative to you. So too does the light from galaxies far, far away, change as they move vast distances in space.
The discovery has been published in the journal Nature.
_______________
The Hubble Search for the Farthest Galaxy in the Universe
______________________________